When I first started working in SEO, I thought a single audit every few months was enough to keep things running smoothly. But I quickly learned that SEO monitoring is where the real wins happen.
Unlike a one-time audit, SEO monitoring is about continuously tracking performance, keyword rankings, backlinks, page speed, and content health, so you can react before issues spiral out of control.
Without it, you’re left guessing why performance dips or why a competitor suddenly outranks you.
And here’s the best part: tools like SEOBoost make continuous monitoring simple.
So, in this guide, I’ll walk you through what SEO monitoring is and the best practices for it.
Let’s start with a definition.
What Is SEO Monitoring?
SEO monitoring means tracking your website’s performance and health on a continuous basis.
That includes:
- Keyword rankings: Are your target keywords moving up or down in the SERPs?
- Backlinks: Are you gaining authority or losing important referring domains?
- Technical health: Are page speed, mobile-friendliness, and Core Web Vitals holding steady?
- Content performance: Which pages are driving organic traffic and which are stagnating?
- SERP features: Are you appearing in snippets, the ‘People Also Ask‘ section, or local packs?
I’ve seen countless businesses lose months of progress simply because they didn’t notice a broken redirect chain, a competitor’s surge in backlinks, or decaying top-performing blog posts.
Continuous monitoring prevents those blind spots.
Why SEO Monitoring Is Important
SEO monitoring helps you plan your content strategy and ensure that it gets you the right results.
It helps you track keyword performance, spot issues early in your content strategy, and gain a better understanding of your competitors and their strategies by comparing them to your own.
Through continuous monitoring, you can see whether a blog post targeting a specific keyword is moving through positions on SERPs. With this information, you can make optimization tweaks to help it rank higher in the top results.
Similarly, identifying issues early on (especially on the technical side) helps you address them promptly.
I’ve seen technical SEO issues cripple sites without anyone noticing.

But with SEO monitoring tools like Google Analytics, you can catch these errors before they cause lasting damage.
You can also use AIOSEO’s SEO Audit Checklist feature, which gives a comprehensive list of factors to check for your website’s performance.
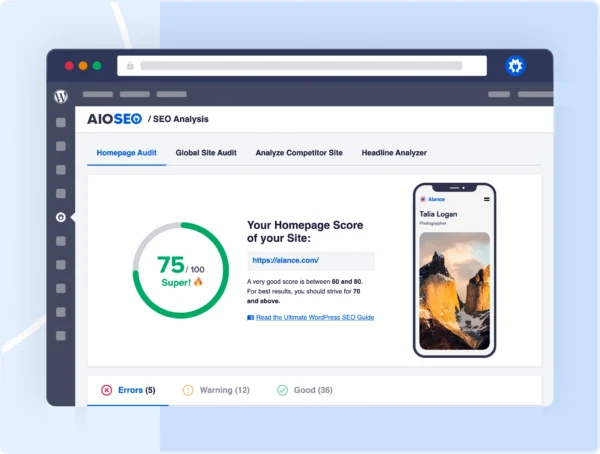
This tool lists errors, warnings, and “good” SEO items on your website, allowing you to prioritize where to focus your efforts.
By monitoring this data, I can easily identify where I’m performing well and where I need to make improvements.
5 Key Metrics to Monitor in SEO
Let’s look at the 6 most important metrics you should monitor at all times.
At SEOBoost, we compile a weekly roundup of these metrics to track improvements or pitfalls over time. You can set up a similar system or monitor them on a monthly basis.
1. Keyword Rankings
What I Watch: Primary keywords, semantically-related secondary keywords, long-tail queries, and ranking changes after algorithm updates
Rankings tell me whether my pages are moving toward the traffic I planned for or drifting away.
To measure quickly and reliably, I use a combination of Semrush and Google Search Console (GSC).
With Semrush’s Position Tracking feature, you can identify how keywords are performing. One feature I like the most is the summary it generates, which gives you a quick overview of what to do.
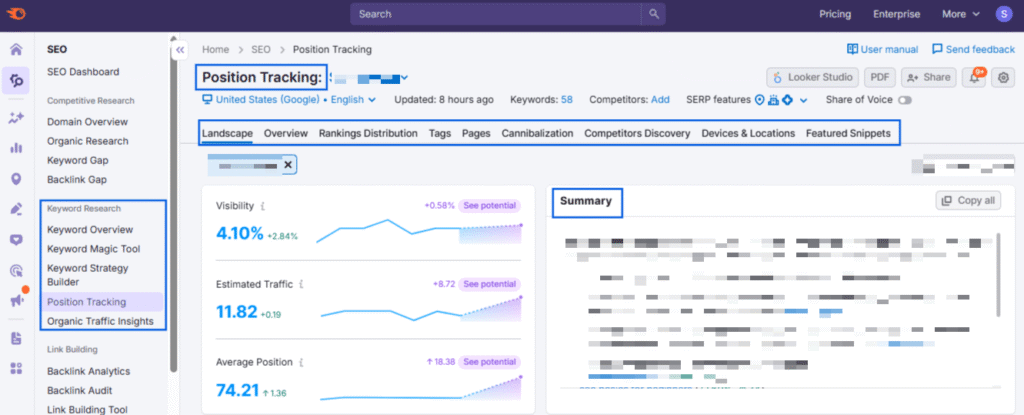
After this, you can cross-check the data by using GSC. Go to Performance and filter by Page to view the queries each URL ranks for, then compare the date ranges.
2. Organic Traffic and Click-Through Rate (CTR)
What I Watch: Organic sessions, impressions, CTR by page and query, device mix
Traffic shows reach; click-through rate (CTR) shows how compelling your result is in the SERP.
To measure organic traffic, use a combination of GSC reports and Google Analytics (GA4) reports.
For GSC, go to performance and view CTR by query to spot headlines/meta that underperform (<2% CTR with high impressions).
You can also view CTR by page and rewrite titles or meta descriptions where impressions are strong but CTR is low.
If you’re using GA4 to track this, go to Reports > Acquisition > Traffic acquisition. Then, set the segment’ Default channel group’ to ‘Organic Search’ and track sessions and conversions.
3. Backlinks and Referring Domains
What I Watch: New/lost referring domains, anchor text balance, link velocity to priority pages
Links still move the needle, especially new referring domains to your best content.
To measure backlinks, you can use GSC for a free, directional view.
Alternatively, you can use Ahrefs or Semrush for a more comprehensive indexing, including monitoring New/Lost and Referring Domains.
To monitor this actively, set alerts if a link is lost or there’s any sudden spike of low-quality links.
4. Content Performance
What I Watch: Engaged sessions, average engagement time, scroll depth (if tracked), conversions/assists, and “decay” over time
If a page doesn’t engage or convert, I flag it for refresh or consolidation.
Here’s how I measure:
- GA4: Engagement > Pages and screens to check engaged sessions and conversions per URL. Add a secondary dimension to the Session default channel to isolate organic traffic.
- GSC: Impressions/clicks by page to confirm search demand is steady (or not).
- SEOBoost Content Audit: Utilize this feature to optimize individual pages.
5. SERP Features
What I Watch: Which features appear for my queries, where I already surface, and which formats competitors own
Owning SERP features (featured snippets, PAA, image/video packs, local) expands visibility beyond “blue links.”
Here’s how to measure (and win the feature snippets):
- GSC: Search Appearance to see special result types you earn.
- Semrush/Ahrefs/Serpstat: To track SERP features by keyword (snippet/PAA/Video/Image/Local pack).
What I do is add a concise 40–60 word definition or answer, or a clean list near the top.
I also turn some of the most relevant People Also Ask questions into FAQs or H3s with clear answers.
Another thing I’ve found helpful is including original images or other forms of multimedia with descriptive filenames, alt text, and surrounding context.
And lastly, don’t forget to add schema markup for specific content types such as How-To or blogs. This will help you stay relevant and increase your chances of ranking with SERP features.
How to Monitor SEO in 5 Simple Steps
Now that we’ve discussed what KPIs to monitor, let’s look into how you can do that.
Here’s the framework I follow:
Step 1: Set Clear Goals
The foundation of effective SEO monitoring is clarity. If you don’t know what you’re measuring, you’ll drown in metrics that don’t matter.
This is why I always start by asking: what’s the outcome we want?
Defining goals this way ensures monitoring aligns with ROI instead of vanity metrics.
Step 2: Build Analytics Dashboards
Switching between GA4, Search Console, and spreadsheets can waste hours. That’s why you should build centralized dashboards.
I recommend using Looker Studio for this purpose.
It allows you to blend GA4 (traffic and conversions) with GSC (impressions and CTR), so you can view the full funnel in one place.
Apart from the analytics dashboard, you can also set up a content dashboard to simplify content production.
This is where using SEOBoost’s Content Management feature can help you get a bird’s-eye view of all content projects and campaigns.
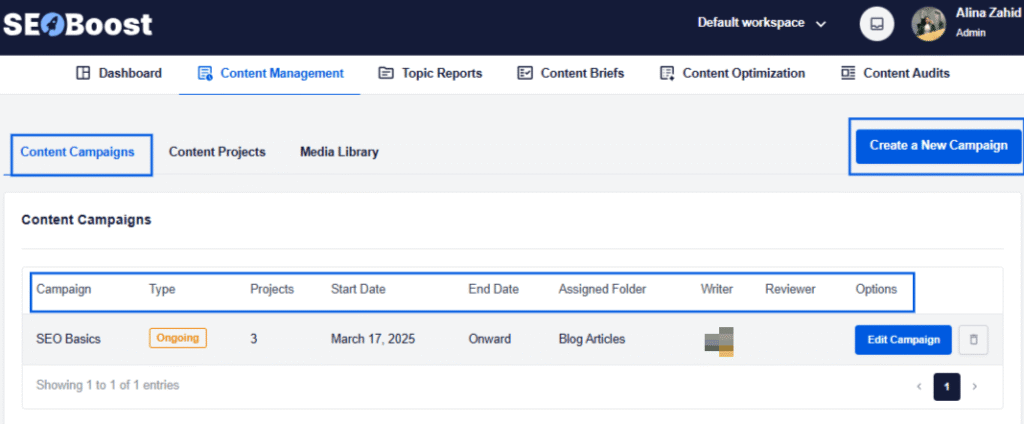
You can see the assigned due dates, reviewers, stakeholders, and content stage.
There’s also a media library that helps you store all content in one place.
Step 3: Establish a Monitoring Cadence
SEO data shifts daily, but reacting to every wobble is a recipe for burnout.
I’d recommend working with 3 levels of cadence:
- Weekly: Check keyword rankings, CTR drops, and critical technical errors.
- Monthly: Review backlinks, Core Web Vitals, and content performance.
- Quarterly: Deep competitor analysis, content gap assessments, and pruning strategies.
This keeps you responsive to changes without getting overwhelmed by daily position changes.
Step 4: Focus on Trends
One mistake I see often is overreacting to short-term fluctuations. Rankings naturally bounce around. The smarter play is to zoom out. I track rolling 4–6 week trends rather than panicking over day-to-day changes.
Instead of rewriting everything at the slightest change in rankings, take the time to understand what has changed and then make an informed decision.
This is where regular monitoring helps you distinguish between a blip and a genuine issue.
Step 5: Take Action on Insights
Monitoring only works if it drives action.
Here’s my rule: every metric tracked should tie to a potential decision.
- If rankings fall: Refresh content and check for cannibalization, or revisit search intent.
- If traffic rises but conversions stay flat: Refine CTAs, adjust page structure, or test offers.
- If backlinks stagnate: Use SEOBoost’s Topic Reports to surface outbound URLs and build a new outreach list.
Treat SEO monitoring as a cycle of goal → measurement → trend analysis → action → repeat.
Without that final step of iteration, monitoring becomes passive reporting instead of an engine for growth.
SEO Monitoring Tools for Optimized Performance
Now, let’s quickly look at the 4 SEO monitoring tools I’d recommend for your day-to-day use.
1. SEOBoost’s Content Audit Feature
When it comes to monitoring content health, SEOBoost is my go-to. Its Content Audit feature is built specifically to track content decay — a phenomenon where once high-performing content slowly loses visibility, rankings, and traffic over time.
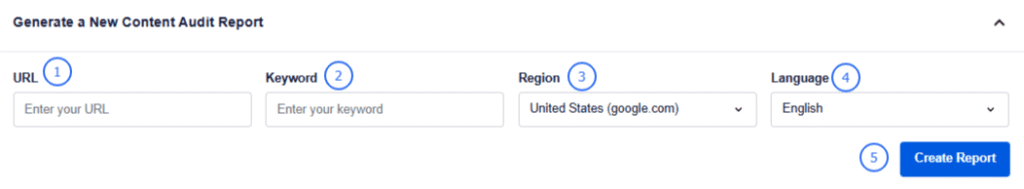
It’s super easy to create a content audit report in SEOBoost. Just insert the URL of the existing content along with the focus keyword you’re trying to optimize for.
Once you do that, it’ll generate a complete report backed by data and recommendations.
How I use it:
- Run regular audits on underperforming content to identify the need for a content refresh.
- Review SEO health scores across my entire content library.
- Get targeted fix recommendations on how to re-optimize the content piece.
This feature eliminates the guesswork in deciding what to update and when.
Pricing: Plans start at $49/month, which includes access to this feature.
2. Google Search Console (GSC)
Google Search Console is the backbone of my monitoring stack because it provides direct data from Google.
Here’s how I use it:
- Track keyword rankings: Monitor impressions, clicks, CTR, and position changes by query.
- Spot technical issues: See indexing problems, mobile usability errors, and structured data warnings.
- Analyze search appearance: Find opportunities in rich snippets, FAQs, or video features.
- Drill down page by page: See which keywords each URL ranks for and where to improve.
Pricing: Free.
3. Looker Studio
Formerly known as Google Data Studio, Looker Studio is my secret weapon for transforming raw data into something usable for stakeholders.
Here’s how to use it:
- Blend GA4 + GSC: Create dashboards that show traffic, conversions, and rankings in one view.
- Visualize trends: Plot 3-month keyword movements to distinguish short-term dips from long-term declines.
- Automate reporting: Clients and teams receive real-time dashboards without needing to send manual reports.
When connected with GSC and GA4, it becomes a powerful command center for decision-making.
Pricing: Free.
4. Serpstat
Serpstat is an affordable, all-in-one SEO platform that I often recommend for smaller teams or agencies that need competitive insights.
Here’s how you can use it:
- Track competitor keyword rankings and movements.
- Audit backlinks and spot new referring domains.
- Run site audits to identify technical SEO issues at scale.
- Monitor SERP features for priority keywords.
Compared to heavier tools like Ahrefs or Semrush, Serpstat is budget-friendly while still covering the essentials.
Pricing: Starts at $59/month.
6 Best Practices for SEO Monitoring
Here are some best practices from my personal playbook that you can start using today.
1. Combine Multiple SEO Tools
No single tool tells the full story.
I use SEOBoost to combat content decay, Google Search Console for rankings, GA4 for traffic and conversions, and Looker Studio to bring it all together.
When I combine these views, I avoid blind spots.
For example, if traffic is up but conversions are flat, GA4 pinpoints the issue. If rankings are stable but impressions drop, GSC shows a SERP change.
This way, I can plan out my SEO strategy with data-driven insights.
2. Focus on KPIs Aligned With Business Goals
It’s easy to get lost in vanity metrics if they’re not tied to a bigger goal you’re trying to achieve.
Data, without direction, is not going to help you achieve your objectives.
Instead, I’d advise tying monitoring directly to business outcomes.
And remember, these outcomes can vary depending on the specific business model. For one client, the KPI might be to increase blog traffic, which contributes to brand awareness. Additionally, it may be demo signups, which can lead to more conversions.
The key is to understand the objectives first and then work around them.
3. Monitor Both Short-Term Fluctuations and Long-Term Trends
Daily SEO data can be noisy, and honestly, you don’t have to track everything every day.
That’s why I balance weekly snapshots (to catch sudden drops or technical issues) with quarterly trend reviews (to see real growth patterns).
This helps me see a progression through the data snapshots and understand trends over time.
4. Set Automated Alerts for Major Changes
One thing you’d likely never want to wake up to as a content strategist is finding out rankings tanked a week ago.
This is why setting up automated alerts is extremely important, so you’re never caught off guard.
You can use SEO tools like GSC, Semrush, or even Looker Studio email alerts to notify you when there’s a sudden traffic drop or CTR dip.
5. Regularly Revisit Content Strategy
SEO monitoring isn’t just reactive; it should guide future strategy.
Every quarter, I’d recommend reviewing the data:
- Which topics are gaining traction?
- Which clusters need fresh supporting posts?
- Which old blogs are dragging down the average?
This way, you can actively shape your editorial calendar according to what’s working on your website.
6. Use SEOBoost’s Content Audit to Combat Content Decay
Content decay is one of the silent killers of SEO. A blog that ranked on page 1 last year might quietly slip to page 3 without you realizing.
Content decay is the gradual decline in a page’s organic traffic, rankings, and visibility over time.
SEOBoost’s Content Audit feature automates this check.
It evaluates the SEO health of each blog post and provides specific recommendations to optimize the SEO score.
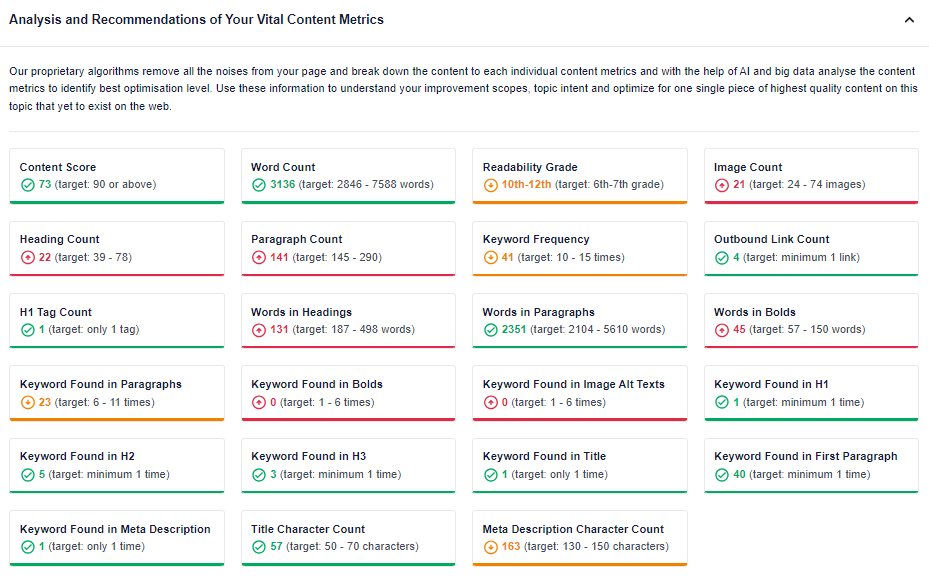
The color-coded report is extremely helpful in identifying areas that need improvement. It helps get your content back on top — something that’s nearly impossible to do manually at scale.
Final Word
Search algorithms evolve, competitors adapt, and content that once performed well can quietly slip into decay. And without continuous SEO monitoring, you’re flying blind.
By using a combination of the monitoring tools mentioned above, you can create a comprehensive 360° monitoring workflow.
But remember, the key isn’t just collecting data, but acting on it.
Track, analyze, and then refine. That’s how you turn monitoring into growth.
FAQs About SEO Monitoring
SEO monitoring is the ongoing process of tracking keyword rankings, traffic, backlinks, technical performance, and content health to ensure your website remains optimized for search engines. Unlike one-time SEO audits, monitoring is continuous and proactive.
The four main types of SEO are:
- On-page SEO, which focuses on optimizing content, keywords, and metadata.
- Off-page SEO, which builds backlinks and authority outside your site.
- Technical SEO to ensure site speed, crawlability, and indexation.
- Local SEO for attracting customers in a specific geographical area.
You can check your SEO score using tools like SEOBoost’s Content Optimization feature, which evaluates on-page elements, keyword usage, content freshness, and overall SEO health of your content.




