When I first started creating SEO strategies, I thought keywords alone were the magic formula. But as Google’s algorithms evolved, I realized that it wasn’t just about keywords, but also about topics and context. That’s where topic modeling comes in.
Topic modeling in SEO helps you uncover connections between terms, organize content more effectively, and build strategies that go beyond simple keyword targeting.
If you’ve ever struggled to structure content around what your audience really wants to know, topic modeling is the missing piece.
So, in this guide, I’ll discuss how you can use topic modeling for SEO planning.
Let’s start with a definition.
What Is Topic Modeling?
Topic modeling is the process of analyzing large amounts of content to automatically detect themes, clusters, and related topics.
Think of it as an AI-powered assistant that reads thousands of pages and says, “Here are the main ideas, and here’s how they connect.”
Now, to understand this better, you must be able to tell keywords and topics apart from one another.
I know this sounds like a given, but it’s good to do a quick review of what they are.
So, keywords are single terms or short phrases (like “SEO tools”). Whereas topics are bigger umbrellas that cluster related keywords and concepts together (like “SEO tools for content optimization, rank tracking, and keyword research”).
You can use keywords to ideate your topic, but at the heart of any great content, there should be a balance of target keywords and the value in content.
Common Topic Modeling Methods
There are several well-known methods that underpin this approach:
- Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA): Focuses on word co-occurrence to uncover relationships.
- Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA): Groups words into “topics” based on patterns found across documents.
- Neural Embedding Models (like BERT): Modern approaches that understand natural language context even better.
You don’t need to be a data scientist to apply these methods directly, as SEO tools already do the heavy lifting. What matters is understanding how topic modeling enhances your content, making it richer, more connected, and easier for search engines to interpret.
The reason why topic modeling matters now is that Google no longer ranks content solely by exact keyword matches. Instead, it employs semantic analysis to gain a deeper understanding of the broader context.
So, when I incorporate topic modeling into my workflow, it ensures that my content aligns with search intent, improves topical relevance, and ultimately establishes my site as a trusted authority in my niche.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using Topic Modeling for Content Planning
Let’s get into my favorite part – a step-by-step guide to how I use topic modeling and so can you.
1. Audit Existing Content
One of the biggest challenges in content marketing is figuring out what to write about next. Topic modeling takes the guesswork out of ideation by surfacing themes and clusters your audience actually cares about.
But every successful content plan starts with knowing what you already have. This is why, I always begin by running a content audit.
I use SEOBoost’s Content Audit feature to do this. With this feature, you get a complete analysis of every blog post, indicating the specific areas for improvement.

This helps you understand which pieces are underperforming, which are outdated, and which could benefit from increased semantic depth.
An audit reveals hidden opportunities in your existing library. Topic modeling adds the “semantic polish” to make underperforming posts competitive again.
2. Collect Competitor Data
Next, I benchmark against competitors. I use Ahrefs Content Explorer and Semrush Topic Research to identify the terms and topics that top-ranking content covers.
I’ve often thought I’ve covered a topic thoroughly, only to discover that competitors are ranking for subtopics I missed. Topic modeling highlights those gaps.
For example, if you’re while researching “AI copywriting tools,” competitor analysis can show strong semantic coverage around other important keywords that your competitors are ranking for.
And by filling these gaps, you not only close the competitive distance but also create a resource that ranks above older, established players.
Pro Tip: Look at the “People Also Ask” section in Google. Often, competitors don’t fully answer those questions, giving you a low-hanging fruit opportunity.
3. Run Topic Modeling Analysis
This is where the real insights come in. Using SEOBoost’s Topic Reports, I plug in a primary keyword and get 7 different types of reports associated with that keyword. This also includes keyword clusters of semantically related terms grouped by keyword intent.

By using these reports, you know exactly what keywords to target, which ones to group and what to add in your brief. This helps you create topic clusters more easily.
And instead of writing one broad, generic blog, you can turn each cluster into its own subtopic and link them together. That approach can help you establish your authority and improve SEO silos or site structure as well.
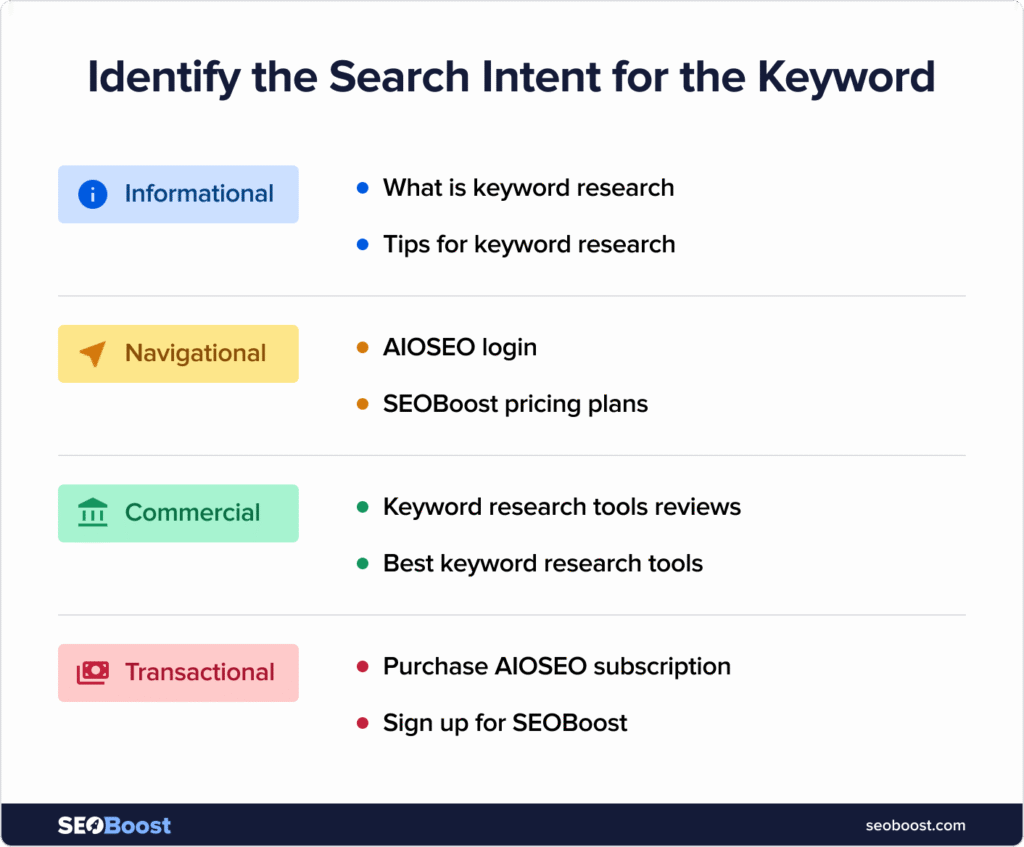
4. Group Topics by Search Intent
Search intent makes or breaks SEO strategy. Topic modeling helps you classify clusters into different type of content that matches and satisfies the intent more clearly.
Remember, Google’s algorithms reward content that satisfies user intent, and topic modeling makes this easier.
By mapping keywords into intent-based clusters (informational, navigational, transactional, and commercial), you can ensure that your content addresses every stage of the customer journey.
This helps you rank for both the evergreen content and the targeted pieces that address your product more clearly.
5. Plan Your Content Calendar
Once I have intent-based clusters, I plug them into a content calendar.
My rule: balance quick wins with long-term authority.
Typically, you should aim to include three types of posts:
- Quick wins or blogs targeting low-competition semantic keywords.
- Authority pieces like pillar posts around high-volume topics.
- Supporting content answering related FAQs and long-tail terms.
Remember, topic modeling is the backbone of effective content clusters. When you build a pillar page, you can also utilize topic modeling insights to identify supporting articles and ensure they interlink naturally.
6. Create Content Briefs
To scale production without losing quality, I rely on SEOBoost’s Content Briefs. These briefs include outlines, semantic terms, and SEO benchmarks to include.

You can also add notes in the brief and share it with your team.
The best part about creating content briefs is that they’re all interlinked with the topic report for the content and the optimization feature, which helps track everything in one place.
4 Tools to Use for Topic Modeling in SEO
Let’s look at the 4 tools I use to make SEO topic modeling easy for me.
1. SEOBoost’s Topic Reports
Whenever I need to plan SEO content at scale, SEOBoost’s Topic Reports are my first stop.
The feature analyzes SERPs in real-time and generates 7 different types of reports for the focus keyword making it easy for you to identify what to target in the content.
It also surfaces important questions to include to win featured snippets and related terms to add for in-depth content coverage.
Pricing: Starts at around $22.50/month for Essentials, with Team ($47.50/month) and Agency ($80.83/month) tiers offering expanded workspaces and usage.
2. LowFruits
I’ve used LowFruits when I want to find semantic opportunities with low competition. It pulls SERP data and groups keywords by intent, highlighting long-tail variations that competitors overlook.
LowFruits reveals untapped, semantically related queries that are often niche areas with far less competition. Targeting those low-hanging fruits can often give you a quick win for organic traffic.
Pricing: It has a pay-as-you-go model.
3. Ahrefs Content Explorer
Ahrefs’ Content Explorer is one of the most powerful ways I’ve found to surface semantic connections in competitive niches.
By plugging in a keyword, I can see which pages are driving traffic, what related terms they use, and how those terms cluster. This data-driven approach made it clear which subtopics I had to include to stay competitive.
Pricing: Starts at $99/month (Lite plan).
4. Semrush Topic Research Tool
When I need to brainstorm quickly around a topic, Semrush’s Topic Research Tool is invaluable. It surfaces clusters of related headlines, subtopics, and frequently asked questions.
These insights help me design a content cluster where each subtopic becomes a supporting blog post.
Pricing: Pro plan at $139.95/month.
Final Word
Topic modeling has completely changed how I approach SEO content planning. Instead of just chasing keywords, I now focus on creating topic-driven, semantically rich content clusters that align with search intent.
By combining audits, competitor analysis, and tools like SEOBoost’s Topic Reports, I can consistently produce content that ranks, resonates with readers, and drives conversions.
The best part?
Topic modeling doesn’t just improve SEO performance, but also future-proofs your content strategy against algorithm updates by ensuring everything you publish is comprehensive, user-focused, and contextually relevant.
FAQs
What is meant by topic modelling?
Topic modeling is a machine learning process that analyzes large sets of content to uncover patterns, themes, and clusters of related terms. In SEO, it helps identify semantically related keywords and content gaps, allowing you to plan more relevant and comprehensive content.
Can ChatGPT do topic modelling?
Yes, ChatGPT and other AI models can simulate topic modeling by analyzing a body of text and surfacing themes or clusters. However, for SEO-specific workflows, tools like SEOBoost, LowFruits, and Semrush are more reliable because they combine AI with real SERP and competitor data.
What is an example of a topic model?
One common method is Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), which groups words into “topics” based on their co-occurrence across documents. For example, if you feed an LDA model 1,000 articles about digital marketing, it might identify topics like SEO tools, content marketing strategies, and social media campaigns. SEO tools build on this logic to cluster keywords and content ideas.